Discover the potential and pitfalls of vertical farming, hailed as the future of agriculture. Learn about its benefits in controlled growing and its challenges such as high energy consumption and environmental concerns. Find out whether this is a viable solution to global food security or a technology that requires critical evaluation.
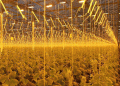
Often hailed as the epitome of agricultural innovation, vertical farming represents a paradigm shift in food production. The promise of year-round, controlled growing in multi-tiered indoor facilities is capturing the imagination of farmers, agronomists and scientists. Beneath the shiny surface, however, lie complexities that require closer attention.
Traditional agriculture faces increasing pressure from climate change, labor shortages and resource depletion. Vertical farming is becoming a beacon of hope, offering solutions to these pressing problems. By isolating crops from external factors and using LED lighting and precise climate control, the company promises to optimize yields with minimal environmental impact.
However, for all its attractiveness, vertical farming has significant drawbacks. High energy demands cast a shadow on sustainability claims. The increased energy consumption associated with LED lighting and environmental control systems not only increases production costs, but also leaves a significant carbon footprint. Additionally, the touted benefits of reducing water use and growing without pesticides are countered by significant energy costs.
The debate over vertical farming goes beyond its environmental impact and concerns its economic viability. While proponents champion its potential to revolutionize global food production, skeptics point out its impracticality in certain contexts. In regions with abundant sunlight and abundant arable land, the economic viability of vertical farming decreases. Moreover, exorbitant initial investment and a limited market for specialty crops hinder its widespread adoption.
As countries face pressure to create sustainable food systems, the role of vertical farming remains controversial. While it holds promise as a complementary solution for urban centers and resource-poor regions, its effectiveness on a large scale requires careful evaluation. Critical considerations include energy efficiency, economic feasibility and environmental impact.