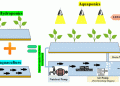
As global data consumption increases, so does the demand for facilities that can store, process, and manage vast amounts of information. Data centers, however, consume significant amounts of energy and generate considerable waste heat. In response to this challenge, companies like atNorth are pioneering new ways to repurpose excess heat and improve energy efficiency.
atNorth, known for its data centers in Iceland, Sweden, and Finland, is set to build its largest data center to date in Ølgod, Denmark. This facility, called DEN02, will serve data-heavy companies and hyperscalers such as cloud service providers and AI-driven enterprises. The first phase, expected to go live by the end of 2026, will have a capacity of 250 megawatts, with further expansion in line with demand.
One of the most exciting aspects of this development is the integration of circular economy principles into the facility’s design. atNorth has partnered with Wa3rm, a leader in waste heat recovery solutions, to repurpose the excess heat generated by the data center. This waste heat will be used to warm nearby residential areas and industrial greenhouses, providing both energy efficiency and environmental benefits. The initiative is part of a growing trend to reduce the carbon footprint of industries by making better use of their byproducts.
Data Center Heat: A Boon for Greenhouse Agriculture
Waste heat recovery is not new, but its application in agriculture is gaining momentum. In Denmark, a country known for its commitment to renewable energy, the DEN02 data center will help support industrial-scale greenhouse farming. By utilizing the data center’s excess heat, local farmers can reduce the need for additional heating sources, thereby lowering energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
Greenhouses, which often require stable temperatures year-round, stand to benefit immensely from this arrangement. The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, further boosts the project’s sustainability. As climate change threatens traditional farming methods, leveraging waste heat offers a way to create resilient agricultural systems that are less dependent on fossil fuels.
Community Benefits: Heating Homes with Data Center Energy
The DEN02 data center will also collaborate with local heating utilities to supply homes in Ølgod with hot water and heating, potentially reducing reliance on conventional heating sources. By reusing waste heat, this project creates a symbiotic relationship between the data center and the surrounding community, enhancing energy security while minimizing environmental impacts. Given Denmark’s colder climate, this strategy is particularly well-suited for the region.
As global energy consumption rises, solutions like atNorth’s DEN02 present a model for other industries to follow. By repurposing heat, not only can companies reduce their environmental impact, but they can also contribute to local economies and promote more sustainable agricultural practices.
atNorth’s DEN02 data center is a groundbreaking example of how industries can merge technological advancements with sustainability. By utilizing waste heat to support both local agriculture and community heating, this project demonstrates the potential of circular economy principles in action. For farmers, agronomists, and agricultural engineers, such innovations offer a glimpse into a future where industrial byproducts can directly contribute to sustainable food production. As climate challenges persist, the integration of energy efficiency and agriculture could become an essential tool for ensuring global food security.