Crop protection
Crop protection best practices and expert advice
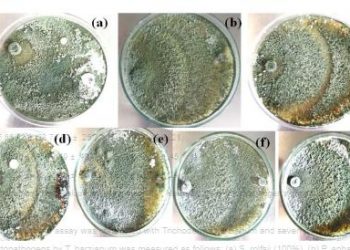
Biological control effect of Trichoderma harzianum against phytopathogens
Chemical pesticides are synthetic substances created to manage plant pests. Frequent chemical usage causes extensive damage to crops and contributes...
Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera; Gelechiidae): a profile of an insect pest and its management methods
South American tomato leafminer, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick, 1917) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), is native to South America, but is a major invasive and quarantine...
Evaluation of the green lacewing, Mallada signatus as a biological control agent for the invasive tomato potato psyllid, Bactericera cockerelli
The tomato potato psyllid, Bactericera cockerelli Šulc, originating from North and Central America, poses a serious threat to Solanaceae crops in Australia....
Single amino acid change in tomato brown rugose fruit virus breaks virus-specific resistance in new resistant tomato cultivar
Tomato cultivation across the world is severely affected by emerging plant viruses. An effective method for protection of commercial crops...
Detection of tomato brown rugose fruit virus in environmental residues
Tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV) is regulated as a quarantine pest in many countries worldwide. To assess whether ToBRFV...
Morphological and molecular characterization of Fusarium incarnatum as a causal disease agent of pepper (Capsicum annuum) fruit rot
Chilli pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is one of the most important commercially cultivated and consumed vegetables in Turkey. During a...
Bacterial contamination in raw fruits and vegetables sold in Delhi, India.
Fresh fruits and vegetables contaminated with microbial pathogens can cause outbreaks of food poisoning and other enteric diseases if consumed...
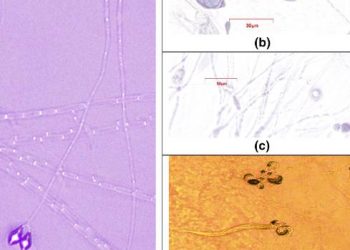
First report of the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys thaumasia in Türkiye and its biocontrol potential against Meloidogyne incognita
Root-knot nematodes, particularly, Meloidogyne incognita, are among the most destructive endoparasitic nematodes, infecting a diverse range of plant hosts. Nematode-trapping fungi...
Performance of biological and chemical nematicides in different soils to control Meloidogyne incognita in tomato plants
Three fluorinated, one carbamate nematicide, as well as two biological control agents were tested in greenhouse trials to determine their...
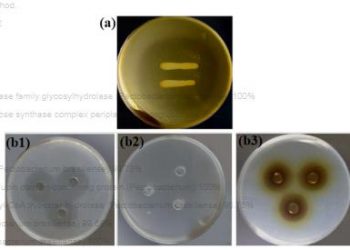
Biological control using Lactobacillus farciminis LJLAB1 against soft rot of postharvest pepper
Soft rot is the most important bacterial disease of postharvest pepper during storage and transportation. Pathogens Pectobacterium carotovorum, Enterobacter sp., Klebsiella sp., Pseudomonas sp. and Bacillus sp. were verified...
BROWSE BY CATEGORIES
- agronomy
- Aquaponics
- Asia
- Climate (meteo)
- Company
- Crop protection
- Cultivation
- Cultivation
- Equipment
- Europe
- Event
- Fertilizers system
- Greenhouse
- horticulture
- Hydroponics systems
- Indoor climates
- Innovation
- Irrigation
- lighting
- Logistics
- Machines
- Machines system
- Management
- Market
- Market Stories
- Marketing
- Organic
- Packaging system
- researches
- Seed
- Soil
- Special Climate
- Suppliers
- Technique system
- Vertical farming
- webinar
BROWSE BY TOPICS
POPULAR NEWS
-
Worldwide session on protecting and harnessing the earth’s biodiversity
-
Tomato Cultivation; Farming Techniques – A Complete Guide
-
Why location and orientation of your greenhouse matter
-
Developing trends in the production of greenhouse vegetables in Russia
-
Greenhouse farming in Turkmenistan: new sanitary regulations set health and safety standards
Recent News
Category
- agronomy
- Aquaponics
- Asia
- Climate (meteo)
- Company
- Crop protection
- Cultivation
- Cultivation
- Equipment
- Europe
- Event
- Fertilizers system
- Greenhouse
- horticulture
- Hydroponics systems
- Indoor climates
- Innovation
- Irrigation
- lighting
- Logistics
- Machines
- Machines system
- Management
- Market
- Market Stories
- Marketing
- Organic
- Packaging system
- researches
- Seed
- Soil
- Special Climate
- Suppliers
- Technique system
- Vertical farming
- webinar